In today’s energy-conscious industrial landscape, efficiency, sustainability, and compliance are non-negotiables. At the core of achieving these goals lies one essential tool: the oxygen bomb calorimeter. This powerful instrument allows engineers and lab technicians to precisely measure the calorific value of fuels — a vital metric for optimizing performance and reducing costs.
Let’s explore how oxygen bomb calorimeters are revolutionizing industrial fuel testing across sectors.
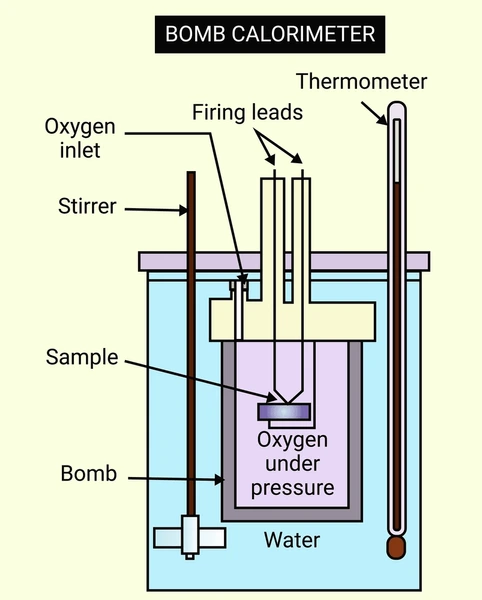
What Is an Oxygen Bomb Calorimeter?
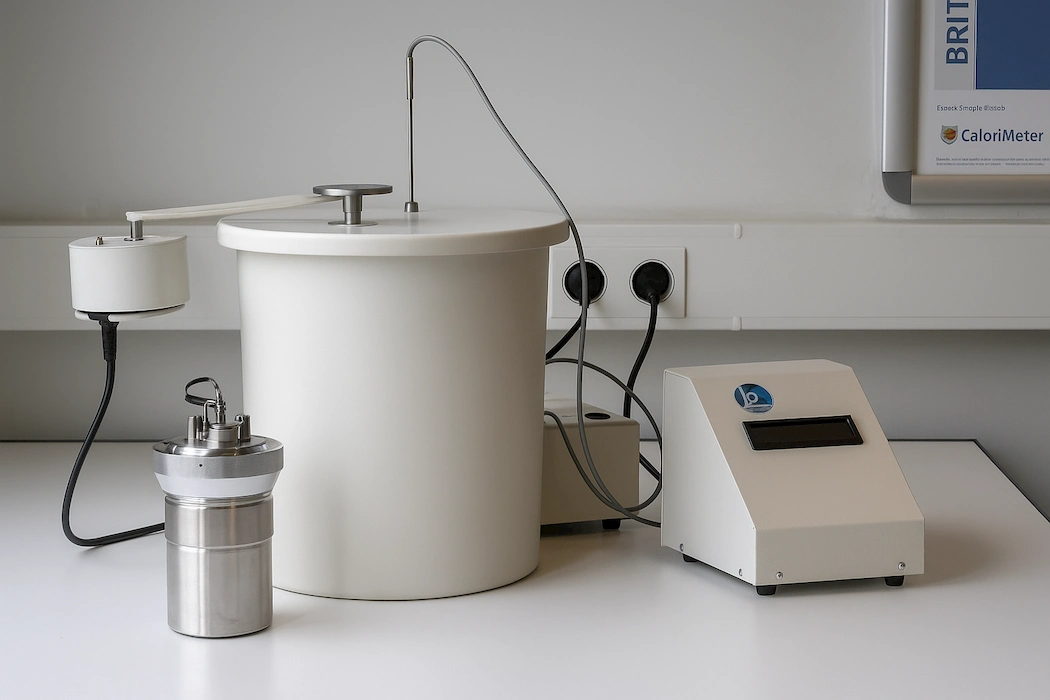
An oxygen bomb calorimeter is a laboratory device used to determine the heat of combustion of a material. This is done by combusting a fuel sample in a sealed, oxygen-rich chamber (“the bomb”) surrounded by water. The heat released raises the water’s temperature, which is then used to calculate the energy content of the sample.
Common units: kJ/kg or BTU/lb
Also known as: Calorific Value or Heating Value (GCV/HHV)
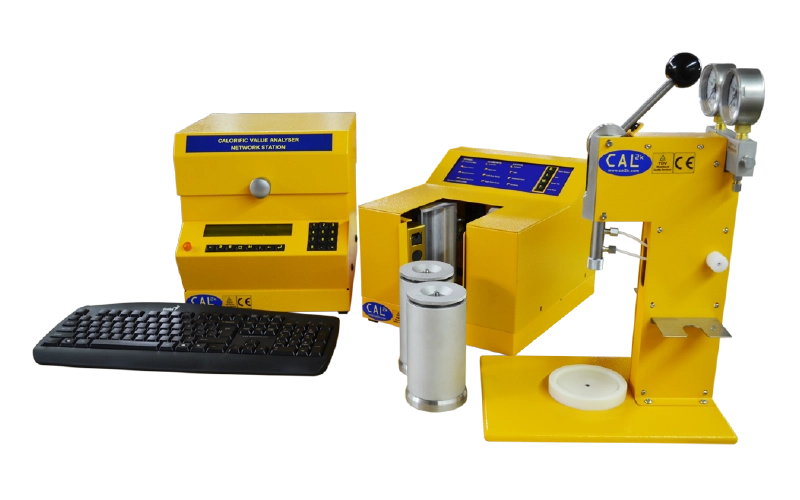

Key Industries That Rely on Oxygen Bomb Calorimeters
Power Generation
- Determines energy content of coal, biomass, and oil.
- Helps fine-tune combustion systems for maximum efficiency.
- Ensures consistency and quality in fuel procurement.
Petrochemical & Refining
- Measures the calorific value of crude oil, diesel, fuel oil.
- Supports quality control during refining and blending.
- Assists in classification and pricing of liquid fuels.
Cement & Steel Manufacturing
- Tests energy potential of coke, coal, and alternative fuels.
- Allows cost-effective fuel blending.
- Supports regulatory reporting on thermal efficiency.
Waste-to-Energy & Biomass
- Determines the combustion potential of refuse-derived fuels (RDF) and biomass.
- Crucial for sustainability metrics and energy recovery operations.
- Assures safety and consistency in waste incineration.
Calorific Value Testing in Food & Biomass: Non-Traditional Uses of Oxygen Bomb Calorimeters
When we think of oxygen bomb calorimeters, industrial applications like coal testing or fuel analysis typically come to mind. But these precision instruments have far wider applications than you might expect. From determining the energy content of food products to analyzing biomass for renewable energy, calorific value testing is quietly transforming several non-traditional industries.
What Is Calorific Value Testing?
Calorific value (also known as energy value or heat of combustion) refers to the amount of energy released when a substance is completely burned in the presence of oxygen. This is typically measured in kilojoules per gram (kJ/g) or kilocalories per gram (kcal/g).
An oxygen bomb calorimeter is the standard instrument used for this purpose. It combusts a small, weighed sample in a sealed, high-pressure chamber filled with oxygen, then measures the heat released by tracking the temperature change in a surrounding water jacket.
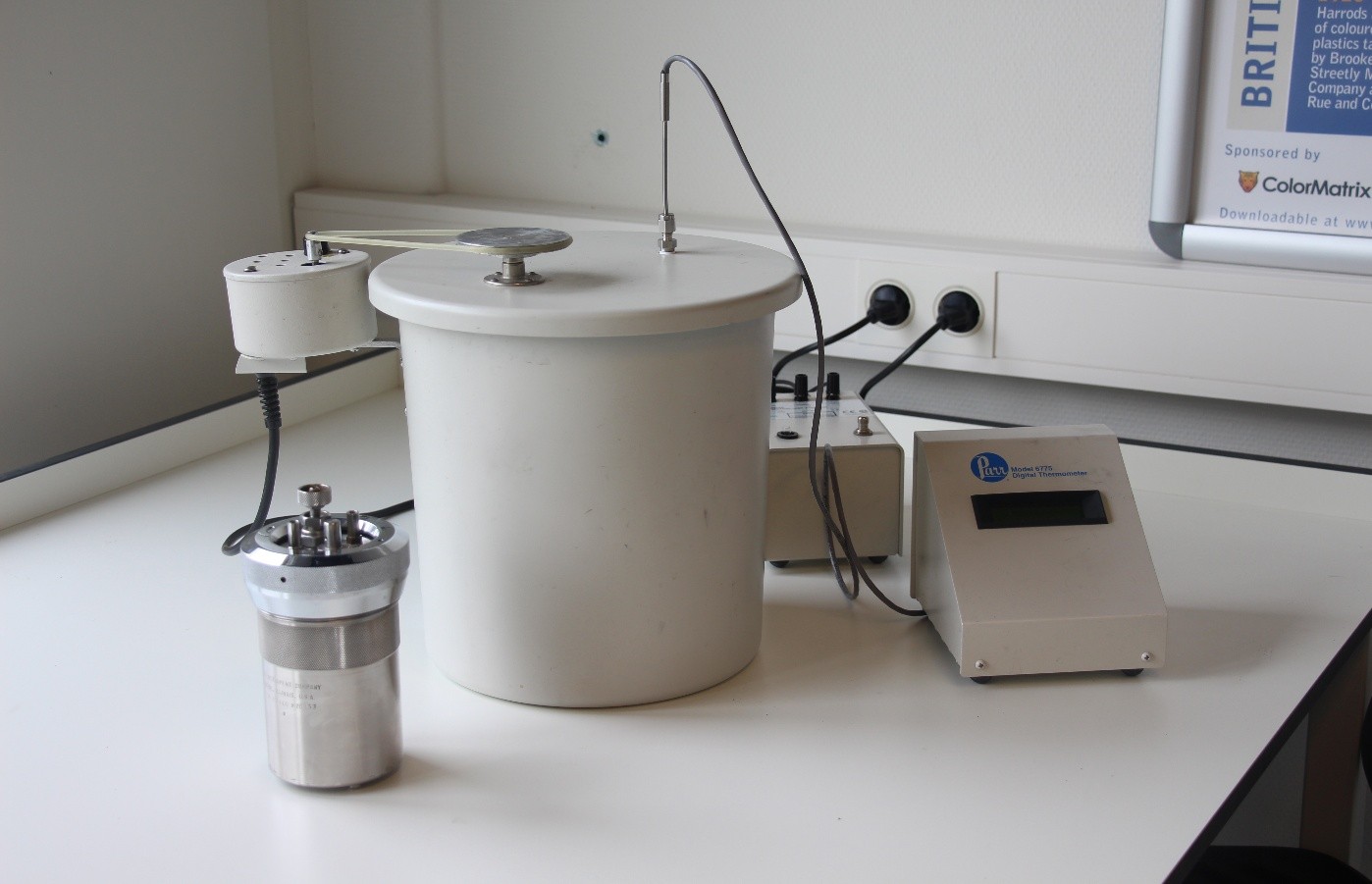

Calorific Value Testing in the Food Industry
Why Measure Energy in Food?
Understanding the energy content of food is vital for:
- Nutritional labeling
- Product development
- Quality control
- Regulatory compliance
Manufacturers are required to list the caloric value of food products on packaging, and oxygen bomb calorimetry is one of the most accurate methods available for determining this.
Applications in Food Testing:
- Processed foods (snacks, baked goods, ready meals)
- Pet foods and animal feed
- Sports supplements and nutrition bars
- Infant formula and dietary products
How It Works:
While there are theoretical calculations based on macronutrient content (protein, fat, carbohydrates), actual bomb calorimetry provides a true measure of metabolizable energy—especially important in complex or multi-ingredient foods.
Calorific Value Testing in Biomass
As the world shifts towards renewable energy, biomass fuels have become key players. However, these materials can vary widely in energy content based on moisture, composition, and processing method. This is where oxygen bomb calorimetry becomes essential.
Common Biomass Samples Tested:
- Wood pellets and chips
- Agricultural waste (husks, stalks, bagasse)
- Algae and aquatic plants
- Refuse-derived fuel (RDF) and organic waste
Benefits of Biomass Calorific Testing:
- Determine energy potential before combustion or gasification.
- Compare fuel sources for efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Validate compliance with international standards (e.g., ISO 18125).
- Improve supply chain quality control in bioenergy production.
Sustainability & Non-Traditional Testing: A Growing Trend
In both the food and biomass industries, there is an increasing emphasis on:
- Waste reduction
- Energy optimization
- Sustainable resource use
Oxygen bomb calorimeters are playing a pivotal role by:
- Helping food producers recover energy from food waste.
- Assisting researchers in evaluating new biomass sources.
- Enabling accurate life cycle assessments (LCA) and carbon footprint analysis.
Did You Know?
Many universities and R&D labs now use bomb calorimeters to:
- Evaluate novel food sources like insect protein.
- Analyze bio-based packaging materials.
- Study food digestibility and metabolic energy in animals.
Modern Calorimeters for Food & Biomass Labs
Today’s oxygen bomb calorimeters are designed for precision, ease of use, and safety. Key features include:
- Automated sample ignition and oxygen filling
- Built-in moisture correction functions
- Compact, benchtop designs ideal for food & bioenergy labs
- Software integration for batch testing and data reporting
These systems allow fast, repeatable testing with minimal operator intervention—ideal for labs processing multiple samples daily.
Why Calorific Value Testing Is Critical
Accurate calorific value testing enables:
- Efficient fuel usage and cost savings
- Environmental compliance (e.g., emissions per MJ)
- Fair trading based on energy content
- Optimized energy-to-output ratios
Even a 1–2% variation in calorific value can significantly impact a plant’s energy balance and profit margins.
Modern Calorimeters: Smarter, Safer, Faster
Today’s oxygen bomb calorimeters are packed with features designed for industrial use and high-throughput labs, including:
- Automated oxygen charging and sample ignition
- Digital data logging with real-time analysis
- Software integration for LIMS and ERP systems
- Built-in safety features (e.g., overpressure protection, auto-shutdown)
These innovations ensure greater consistency, faster throughput, and improved lab safety.
Real-World Impact: Efficiency Meets Sustainability
By providing precise energy measurements, bomb calorimeters support:
- Improved combustion performance
- Lower emissions per unit of energy
- Better fuel procurement decisions
- Compliance with ISO, ASTM, and EPA regulations
For any industrial lab, it’s a tool that delivers both operational and environmental ROI.
CONCLUSION:
Oxygen bomb calorimeters are indispensable in modern industrial labs. From coal testing in power plants to biofuel analysis in sustainable energy labs, they provide the accurate calorific data required to make informed decisions and optimize processes.
From calculating the calories in your snack bar to evaluating the heat output of wood pellets, oxygen bomb calorimeters are proving their value well beyond traditional fuel testing. In industries where energy measurement, efficiency, and sustainability intersect, this powerful instrument continues to deliver critical data that drives smarter decisions.
Whether you’re in food manufacturing, animal nutrition, biomass research, or biofuel production, accurate calorific value testing is no longer optional—it’s essential.
General FAQs About Oxygen Bomb Calorimeters in Food, Biomass & Industrial Fuel Testing
- What is an oxygen bomb calorimeter?
An oxygen bomb calorimeter is a laboratory device used to measure the calorific value (or energy content) of a sample by combusting it in a high-pressure, oxygen-rich environment and measuring the resulting heat released.
- What is calorific value?
Calorific value is the amount of heat energy released when a substance is completely burned. It’s typically expressed in kJ/g, kJ/kg, or kcal/g, and is a critical indicator of fuel or food energy potential.
- How is a sample tested in a bomb calorimeter?
The sample is placed in a sealed “bomb” chamber filled with oxygen, ignited electrically, and the heat released is absorbed by surrounding water.
- What types of materials can be tested in a bomb calorimeter?
Materials like coal, diesel, biomass, wood pellets, food products, animal feed, waste-derived fuels, and even explosives can be tested, depending on the calorimeter’s specifications.
Fuel & Industrial Testing FAQs
- Why is calorific value testing important in industrial fuel analysis?
It helps in assessing fuel quality, combustion efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and regulatory compliance for industries like power generation, steel, cement, and refining.
- What’s the difference between Gross and Net Calorific Value?
- Gross Calorific Value (GCV) includes the total heat released, including the condensation of water vapor.
- Net Calorific Value (NCV) excludes the latent heat of vaporization.
Both are used based on industry standards and application.
- Can bomb calorimeters be used for liquid fuel testing?
Yes. With appropriate sample containers and accessories, bomb calorimeters can test diesel, fuel oil, alcohol, and other liquid fuels.
- Are bomb calorimeters compliant with ISO and ASTM standards?
Yes. High-quality instruments comply with standards like ISO 1928, ASTM D5865, ASTM D240, and others, depending on the sample type and application.
Food & Biomass Testing FAQs
- How is calorific value testing used in the food industry?
It’s used to determine the energy (calorie) content of foods for nutritional labeling, product formulation, and regulatory compliance.
- Is calorimetry more accurate than nutritional calculations?
Yes. Calorimetry provides direct measurement of energy content, unlike theoretical calculations which estimate values based on nutrient composition.
- What food products are typically tested with bomb calorimetry?
Common examples include snacks, cereals, energy bars, pet foods, animal feed, baby formula, and processed meals.
- Why test biomass for calorific value?
To determine the energy potential of renewable fuels like wood pellets, agricultural waste, algae, and refuse-derived fuel, enabling more efficient energy production and compliance with sustainability targets.
- How does moisture content affect biomass calorific value?
Higher moisture reduces the effective energy output because part of the combustion energy is used to evaporate water. Moisture correction is essential for accurate testing.
Technical & Operational FAQs
- What features should I look for in a modern bomb calorimeter?
Key features include:
- Automatic oxygen filling & ignition
- High-resolution temperature sensors
- Moisture correction capability
- User-friendly software for analysis & reporting
- Safety features like overpressure protection
- Is training required to operate a bomb calorimeter?
While modern systems are user-friendly, basic lab training is recommended for sample handling, calibration, safety procedures, and interpreting results accurately.


Ready to Improve Fuel Testing in Your Lab?
At APEX INSTRUMENT, we provide state-of-the-art oxygen bomb calorimeters designed for precision, reliability, and ease of use in industrial environments.
Explore Our Calorimeter Range
Request a Demo or Consultation
Contact Our Technical Team
Contact :
- Mobile/WhatsApp: +971526191767
- Email: sales@apex-instrument.com



